Compute Add-ons
Every project on the Supabase Platform comes with its own dedicated Postgres instance running inside a virtual machine (VM).
The following table describes the base instances, Nano (free projects) and Micro (paying projects), with additional compute add-ons available if you need extra performance when scaling up Supabase.
Upgrade to Micro Instances at No Additional Charge for Paid Projects
If you upgraded your Supabase organization from the Free plan to a paid plan, any projects created on the Free plan will remain on Nano instances due to the upgrade process incurring downtime.
Since every project on a paid plan is already paying for a Micro instance you can upgrade to Micro at no additional charge. See Supabase Pricing for more information.
We recommend that you take advantage of the upgrade when your usage requires Micro resources because the upgrade incurs downtime.
| Compute Size | Hourly Price USD | Monthly Price USD | CPU | Memory | Database Max Connections1 | Connection Pooler Max Clients | Max DB Size (Recommended)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano3 | $0 | $0 | Shared | Up to 0.5 GB | 60 | 200 | 500MB |
| Micro | $0.01344 | ~$10 | 2-core ARM (shared) | 1 GB | 60 | 200 | 10GB |
| Small | $0.0206 | ~$15 | 2-core ARM (shared) | 2 GB | 90 | 400 | 50GB |
| Medium | $0.0822 | ~$60 | 2-core ARM (shared) | 4 GB | 120 | 600 | 100GB |
| Large | $0.1517 | ~$110 | 2-core ARM (dedicated) | 8 GB | 160 | 800 | 200GB |
| XL | $0.2877 | ~$210 | 4-core ARM (dedicated) | 16 GB | 240 | 1,000 | 500GB |
| 2XL | $0.562 | ~$410 | 8-core ARM (dedicated) | 32 GB | 380 | 1,500 | 1TB |
| 4XL | $1.32 | ~$960 | 16-core ARM (dedicated) | 64 GB | 480 | 3,000 | 2TB |
| 8XL | $2.562 | ~$1,870 | 32-core ARM (dedicated) | 128 GB | 490 | 6,000 | 4TB |
| 12XL | $3.836 | ~$2,800 | 48-core ARM (dedicated) | 192 GB | 500 | 9,000 | 6TB |
| 16XL | $5.12 | ~$3,730 | 64-core ARM (dedicated) | 256 GB | 500 | 12,000 | 10TB |
Compute sizes can be changed by first selecting your project in the dashboard here and the upgrade process will incur downtime.
We charge hourly for additional compute based on your usage. Read more about usage-based billing for compute.
Dedicated vs. shared CPU
All Postgres instances on Supabase are dedicated applications running inside dedicated virtual machines. However, the underlying hardware resources, for example the physical CPU, may be shared between multiple VMs, but appear to the OS as if it is a dedicated hardware CPU. This is commonly referred to as a vCPU (virtual CPU). Cloud providers use these shared hardware resources to save cost—you can upgrade to a larger compute add-on to guarantee a dedicated physical CPU for your instance.
Compute upgrades
When considering compute upgrades, assess whether your bottlenecks are hardware-constrained or software-constrained. For example, you may want to look into optimizing the number of connections or examining query performance. When you're happy with your Postgres instance's performance, then you can focus on additional compute resources. For example, you can load test your application in staging to understand your compute requirements. You can also start out on a smaller tier, create a report in the Dashboard to monitor your CPU utilization, and upgrade later as needed
Disk IO
SSD disks are attached to your servers, and their performance depends on the compute add-on of your instance as well as the attributes set for the disk.
Disk I/O Metrics:
- Throughput: Measured in Megabits per Second (Mbps), which indicates the rate of data transfer.
- IOPS: Input/Output Operations per Second, which measures the number of read and write operations.
Performance Limits:
Disk throughput is capped at 19,000 Mbps and IOPS is capped at 80,000 IOPS for all compute add-ons.
| Compute add-on | Max Disk Throughput | Baseline Disk Throughput | Max IOPS | Baseline IOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano (free) | 2,085 Mbps | 43 Mbps | 11,800 IOPS | 250 IOPS |
| Micro | 2,085 Mbps | 87 Mbps | 11,800 IOPS | 500 IOPS |
| Small | 2,085 Mbps | 174 Mbps | 11,800 IOPS | 1,000 IOPS |
| Medium | 2,085 Mbps | 347 Mbps | 11,800 IOPS | 2,000 IOPS |
| Large | 4,750 Mbps | 630 Mbps | 20,000 IOPS | 3,600 IOPS |
| XL | 4,750 Mbps | 1,188 Mbps | 20,000 IOPS | 6,000 IOPS |
| 2XL | 4,750 Mbps | 2,375 Mbps | 20,000 IOPS | 12,000 IOPS |
| 4XL | 4,750 Mbps | 4,750 Mbps | 20,000 IOPS | 20,000 IOPS |
| 8XL | 9,500 Mbps | 9,500 Mbps | 40,000 IOPS | 40,000 IOPS |
| 12XL | 14,250 Mbps | 14,250 Mbps | 50,000 IOPS | 50,000 IOPS |
| 16XL | 19,000 Mbps | 19,000 Mbps | 80,000 IOPS | 80,000 IOPS |
Self-Serve Configurability
You can now adjust storage type, IOPS, throughput and disk size parameters yourself through the Dashboard here.
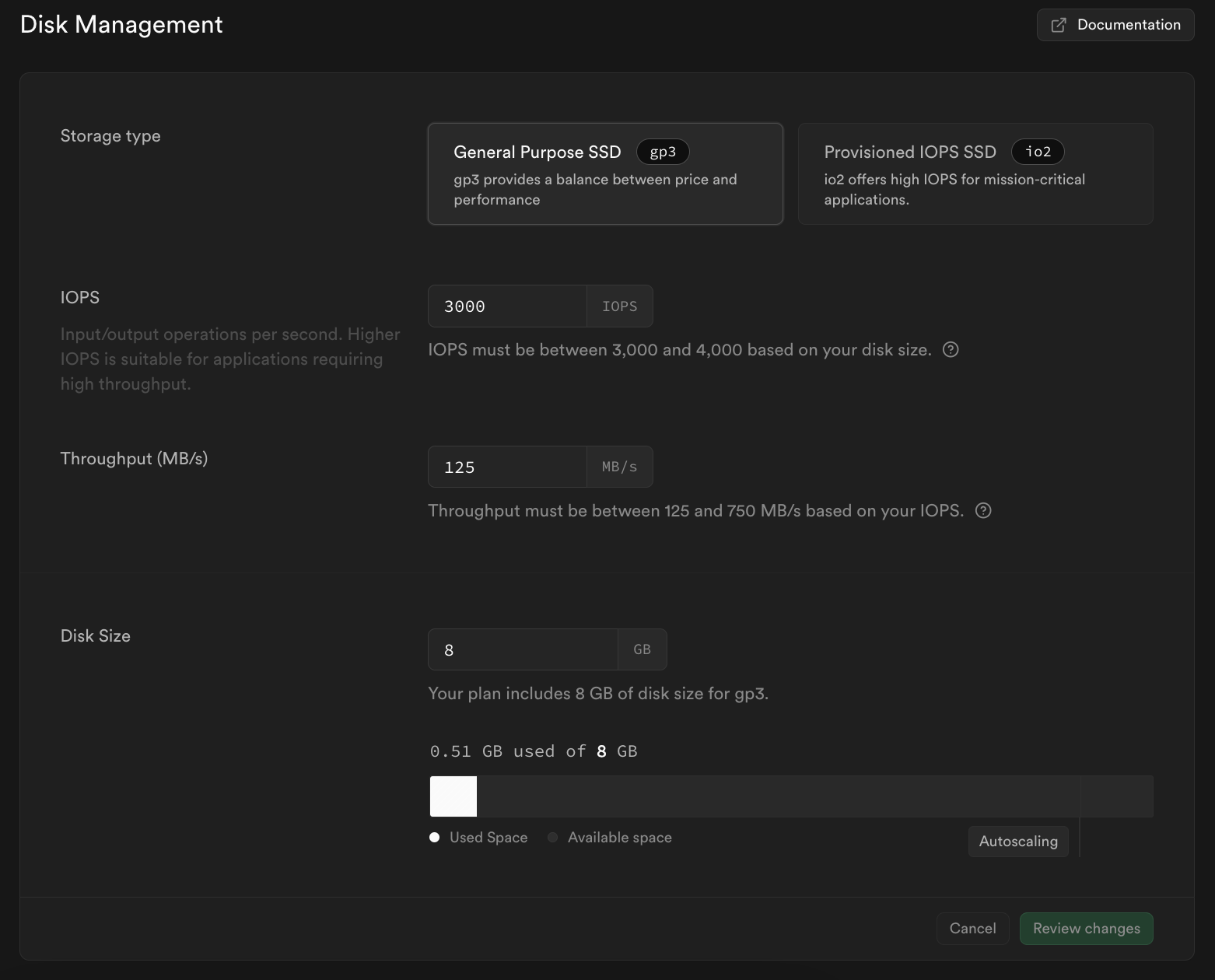
Be aware that increasing IOPS or throughput incur additional charges.
Understanding I/O Balance and Bursting (Smaller add-ons)
For smaller add-ons like Nano, Micro, and Small, you get I/O balance and burst capacity. These add-ons have limited base performance for IOPS and throughput. However, they come with burst credits that let you handle temporary spikes for 30 minutes in a day in demand by briefly exceeding their baseline performance. This means you can achieve higher performance for short bursts before reverting to your baseline limits.
For example, the micro add-on can burst up to 2,085 Mbps for 30 minutes a day and reverts to the baseline performance of 87 Mbps. Your disk IO budget gets replenished throughout the day.
Dedicated I/O Resources (Larger add-ons)
Larger add-ons, such as 4XL and above, come with dedicated I/O resources and don't rely on I/O balance or burst capacity. These add-ons are designed for sustained, high performance with specific IOPS and throughput limits. They provide consistent performance without needing to burst. If you hit your IOPS or throughput limit, throttling will occur, but you won't have burst credits to exceed these limits.
Storage Volume Types: gp3 vs. io2
When selecting your storage volume, it’s essential to focus on the performance needs of your workload. Below is a comparison between the two main volume types we offer:
gp3 (General Purpose SSD) - Default Option This is our standard, versatile option and offers great value for most use cases. It’s ideal for general workloads that require moderate IOPS and throughput, such as small to medium-sized databases, development environments, and everyday tasks.
- Volume Size: Up to 16TB
- IOPS: 3,000 (default) up to 16,000 (maximum)
- Throughput: 125 MB/s (default) to 1,000 MB/s (maximum)
io2 (Provisioned IOPS SSD) This option is designed for high-performance needs where low latency and very high IOPS are crucial. If you’re running large-scale databases or mission-critical applications, io2 provides the performance you need.
- Volume Size: Up to 60TB
- IOPS: Can scale up to 256,000 based on your disk attributes
- Throughput: Scales with IOPS
Choosing the Right Type Think about the performance your workload demands. For general, day-to-day operations, gp3 should be more than enough. If you need high throughput and IOPS for critical systems, io2 will provide the performance required.
Choosing the Right Compute Add-On for Consistent Disk Performance
If you need consistent disk performance, choose the 4XL or larger compute add-on which has the same baseline and maximum disk throughput and IOPS.
If you're unsure of how much throughput or IOPS your application requires, you can load test your project and inspect these metrics in the Dashboard. If the Disk IO % consumed stat is more than 1%, it indicates that your workload has burst beyond the baseline IO throughput during the day. If this metric goes to 100%, the workload has used up all available disk IO budget and will revert to baseline performance. Projects that use any disk IO budget are good candidates for upgrading to a larger compute add-on with higher baseline throughput.
Compute add-on changes will not cause you to lose your disk attributes.
Constraints
- After any disk attribute change, there is a cooldown period of approximately six hours before you can make further adjustments. During this time, no changes are allowed. If you encounter throttling, you’ll need to wait until the cooldown period concludes before making additional modifications.
- You can increase volume size but cannot decrease it.
- The performance of EBS volumes is affected by the add-on size to which you are attached.
Postgres replication slots and WAL senders
Replication Slots and WAL Senders are used to enable Postgres Replication.
The maximum number of replication slots and WAL senders depends on your compute add-on size, as follows:
| Compute add-on | Max Replication Slots | Max WAL Senders |
|---|---|---|
| Nano (free) | 5 | 5 |
| Micro | 5 | 5 |
| Small | 5 | 5 |
| Medium | 5 | 5 |
| Large | 8 | 8 |
| XL | 24 | 24 |
| 2XL | 80 | 80 |
| 4XL | 80 | 80 |
| 8XL | 80 | 80 |
| 12XL | 80 | 80 |
| 16XL | 80 | 80 |
As mentioned in the Postgres documentation, setting max_replication_slots to a lower value than the current number of replication slots will prevent the server from starting. If you are downgrading your compute add-on, please ensure that you are using fewer slots than the maximum number of replication slots available for the new compute add-on.
Upgrade downtime
Compute add-on changes are usually applied with less than 2 minutes of downtime, but can take longer depending on the Cloud Provider.
Footnotes
-
Database max connections are recommended values and can be customized depending on your use case. ↩
-
Database size for each compute instance is the default recommendation but the actual performance of your database has many contributing factors, including resources available to it and the size of the data contained within it. See the shared responsibility model for more information. ↩
-
Nano compute resources on the Free plan are subject to change. ↩